What is enterprise project portfolio management (EPPM)?
EPPM is a higher-level, more integrated type of project portfolio management (or product portfolio management). It involves breaking an enterprise organization’s strategy and operations into smaller initiatives or groups—often called portfolios. Stakeholders across several teams, departments, and locations will have visibility of these initiatives. They can then assign, complete, and review them accordingly.
EPPM takes a holistic, overarching view of managing all the projects and investments a business is undertaking simultaneously. For example, a company may have new product portfolios, cost-saving project portfolios, in-market product portfolios, and technology portfolios. Because EPPM operates at an enterprise level, it encompasses all—or at least the majority—of these different portfolios.
What are the key elements of EPPM?
While every project, portfolio, and department has unique requirements, EPPM ensures everything is working to support broader business goals. It focuses on delivery and alignment with the organization’s strategic objectives. Key elements of the EPPM approach include:
- A well-defined strategy that communicates corporate objectives, budget prioritization, standardized project and proposal evaluations, and more.
- Project and financial forecasting, including projecting ROI
- Cost reduction by eliminating duplicate efforts, streamlining execution, tracking progress, and monitoring cost and revenue
- Cross-functional resource prioritization and dependency planning to improve productivity
- Business intelligence and analytics to inform decisions
- Implementation of agile and “always improving” culture
Successful EPPM provides businesses with effective frameworks and standards to create a centralized and comparable view of all projects across different portfolios and divisions. It integrates people and activities at an enterprise level to generate business value.
What types of organizations are suited to EPPM?
Because of the challenges that EPPM aims to solve, it is suited to large, complex organizations with sophisticated requirements and diverse portfolios of projects. It can be particularly helpful for those in volatile industries where risk mitigation is a key consideration and products are ever-changing.
A good example includes life sciences and pharmaceuticals, where NPD is characterized by strict regulatory requirements and high research and development (R&D) costs.
Aerospace and defense—where large-scale projects require long development cycles, stringent compliance, and significant investment in advanced technologies—is another.
Organizations in the engineering and construction sectors can also benefit from EPPM. It is a sector with operations subject to long timelines, regulatory compliance, and significant capital expenditure and investment.
What are the benefits of EPPM?
Put simply, enterprise project portfolio management enables organizations to manage and oversee many project portfolios simultaneously from a higher level, providing:
- Real-time, accurate data that informs decision-making and empowers you to prioritize projects
- A centralized view of the needs and requirements of the whole company, promoting strategic alignment and scalability
- Better insight and tools to manage budgets, resources, assignments, and capacity
- Visibility of potential delays, risks, or duplicate tasks
- Information required to understand revenue attribution of projects and communicate with stakeholders
The enterprise portfolio management office (EPMO): roles and responsibilities
The EPMO is a senior leadership team overseeing the EPPM process. More centralized and geared towards strategic objectives and alignment than a typical PMO, the EPMO coordinates at the enterprise level.
The EPMO maintains a high-level view of all projects, ensuring that business outcomes align with its key objectives and that value and benefits are realized. It is concerned with overarching portfolio visibility, strategic alignment, resource optimization, and performance tracking. Some of the critical responsibilities might include:
- A leader, “head,” or director of EPPM oversees the entire approach. This will include implementing best practices, setting goals, and ensuring activities align with business objectives.
- Portfolio managers are in charge of one specific portfolio. Their role will include project selection and prioritization, resource allocation, and more.
- Project managers are leaders of individual projects or tasks within a portfolio. They are responsible for project execution and success.
EPMO members may also be members of the C-suite, but every business is different, and in turn, so is every EPMO. More responsibilities of the leader of an EPMO can include:
- Portfolio governance
- Project forecasting to determine success or failure
- Tracking projects against objectives and KPIs
- Ensuring an understanding of priorities based on broader business goals
- Improving the visibility of projects across the entire organization
- Facilitating communication
- Providing accessible, accurate data to inform business decisions
- Building and promoting agility across the enterprise
What’s the difference between EPPM and PPM?
Traditional project portfolio management (PPM) focuses on project delivery at a business level, but EPPM takes a top-down approach. Rather than overseeing one portfolio of projects within one specific area of the business, all of which share a similar goal or outcome, EPPM refers to managing a business’s entire suite of project portfolios simultaneously.
For example, larger enterprise organizations may have company-wide digital transformation projects and new product development split between business-to-business (B2B) and government ICPs. It can therefore be challenging to see, measure, and track the business impact of very different projects when assessed in silos. EPPM allows leaders to connect dots across the entire organization, gaining clear insights into progress and blockers.
This way, key decision-makers can accurately oversee multiple initiatives in the context of the enterprise and make better-informed decisions.
EPPM tools and software
Modern EPPM involves the comprehensive, real-time collection of data and is most often discussed in relation to the strategic use of integrated PPM tools. These are software suites that provide comprehensive visibility of resources, progress, and objectives across an organization from a high-level, global standpoint.
By consolidating and centralizing large quantities of data about interdependent projects, programs, and tasks in a single, enterprise-wide system, EPPM tools create a single source of truth across all project portfolios, minimizing the risk of errors and discrepancies. They help project managers understand the dependencies between projects and coordinate all resources across the business.
For a real-world example, check out how Teva created a single source of truth for their strategic portfolio management practices, consolidating 17 tools into one.
Ultimately, EPPM tools enable enterprise organizations to save money, reduce risks, minimize human error, and speed up digital transformation. They help to ensure that projects are completed at the enterprise level, within time and budget. The clarity and visibility they provide, particularly to senior leaders, C-Level stakeholders, and executives, can guide decision-making regarding budget and resources to maximize profitability, helping organizations stay agile.
Most project management software and tools improve the handling of single projects, focusing on individuals and resources. Essentially, they’re not designed for efficiently overseeing multiple complex projects throughout their lifecycle–an issue that EPPM software aims to solve.
Features and capabilities
EPPM tools help with every aspect of managing, running, coordinating, and prioritizing a collection of projects, programs, portfolios, and initiatives. They cover the entire range of project management activities and capabilities, from goal setting to performance reporting.
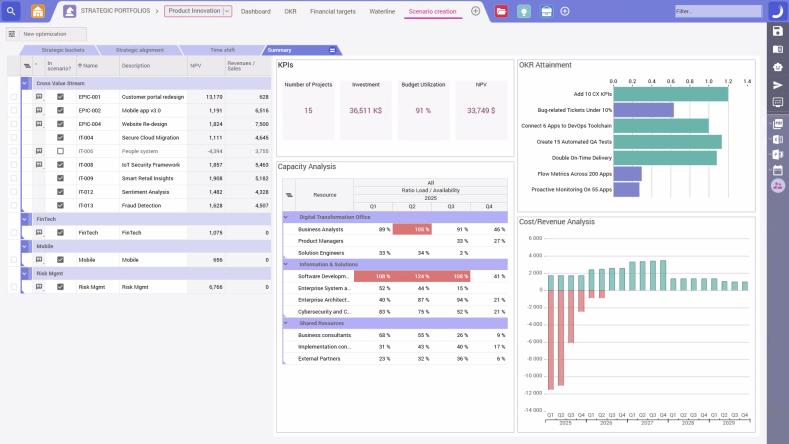
Resource management
EPPM tools help ensure resources—financial, technical, and human—are allocated and distributed in the most optimal way to maximize portfolio value and ensure the business prioritizes the highest-value projects.
These tools have capacity planning features, which help decision-makers to anticipate bottlenecks or space capacity across certain roles, skills, and departments. The software can be integrated with other systems and solutions as part of a fully-connected ecosystem.
Financial oversight and reporting
EPPM tools have sophisticated reporting and analytics capabilities. Drill-down features and configurable, customizable dashboards give dynamic visualization of data across a project, program, or portfolio, helping with forecasting and evaluation of revenues, ROI, and profitability. Armed with these powerful, real-time insights, EPPM tools empower leaders to identify issues before they become critical.
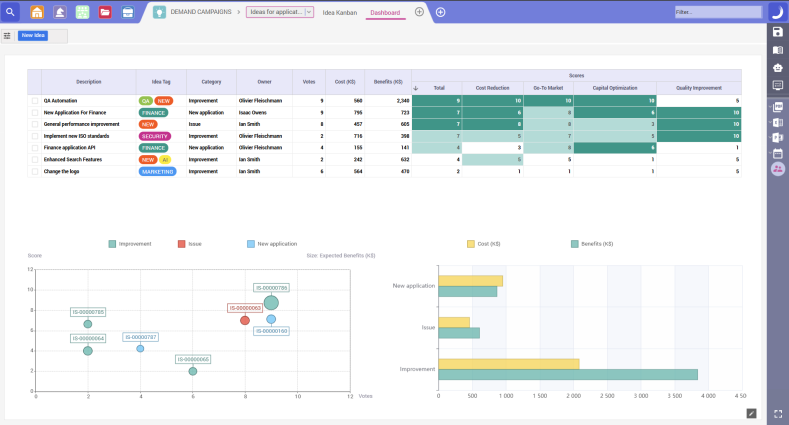
Risk management
EPPM tools help organizations identify risks early and implement necessary mitigation strategies. The aforementioned financial insights, along with automated risk-driven detection and analysis, help project managers gauge confidence levels for (and the viability of) projects.
Many also have dynamic and advanced “what-if” scenario-building capabilities, allowing decision-makers to model certain actions and evaluate impact and risk.
Strategic management and alignment
EPPM tools help leaders identify those projects that best align with an organization’s broader goals and objectives. Real-time insights enable leaders to track progress and adapt if necessary.
They can also flexibly facilitate a range of project management methodologies and their frameworks. Organizations may employ traditional, sequential methodologies like waterfall or agile methodologies, like Scrum and Kanban—possibly a mixture of both. Fully scalable, these tools can also grow with the organization without the need for wholesale changes or investment.
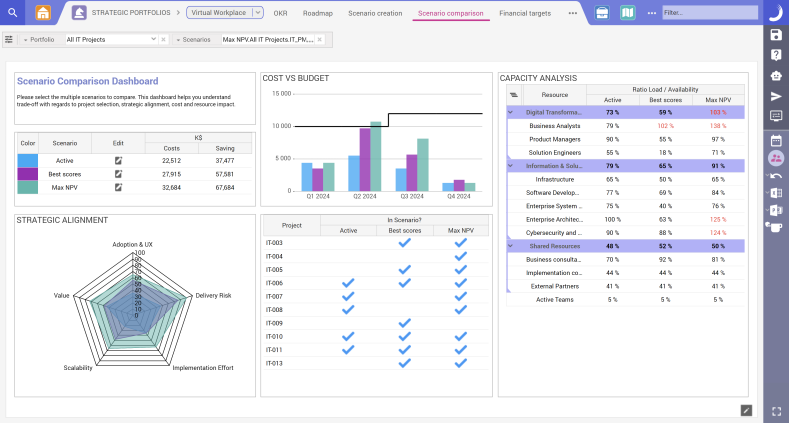
Scenario comparison in Planisware.
Collaboration and support
A fully-integrated EPPM solution—with a single source of truth—can break down silos, minimize errors, and promote communication, collaboration, and transparency.
Additionally, most modern EPPM tools are cloud-based, negating the need for physical on-site servers, firewalls, and shared databases. This enables virtual and disparate teams to access the same information in real time, regardless of location, keeping teams aligned and engaged throughout the lifetime of projects.
Adopting EPPM software for the first time inevitably raises many questions. These tools come with a vendor commitment to offer deployment support and end-user training. Responsive, ongoing human support, from a partner with a history of successful implementations, helps smooth the deployment process.
Trusted by global organizations, Planisware is a leading solution for maximizing the value of projects, programs, and portfolios at an enterprise level. Start your organization’s journey to a more mature, optimized, integrated, and profit-driving strategy—request a demo today.


